Collection과 Map
Java의 자료구조는 크게 Collection과 Map으로 나눌 수 있음
그리고, Collection은 List와 Set, Queue로 나눌 수 있음
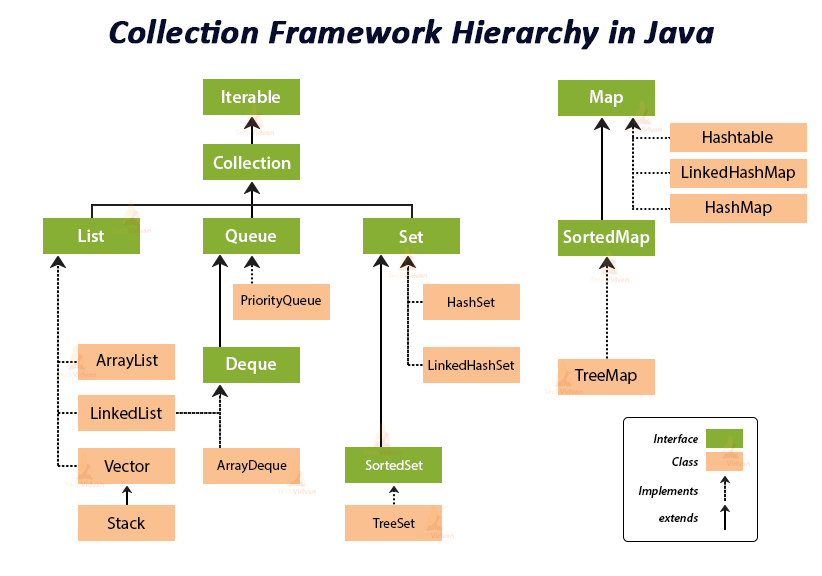
본 글에서는 아래 자료구조에 대한 내용을 간단히 정리한다.
List: ArrayList, LinkedList, Vector, StackSet: HashSet, LinkedHashSet, TreeSetQueue: priorityQueue, ArrayDequeMap: HashMap, LinkedHashMap, Hashtable, TreeMap
Collection - List
리스트는 순서를 가지고, 원소의 중복이 허용된다는 특징이 있음
ArrayList
ArrayList는 배열을 이용하여 만든 리스트이다.
- 기본 크기는 10이지만, 원소가 늘어나면 더 큰 배열에 옮겨닮는다.

배열의 특징 때문에 조회가 빠르다는 장점이 있지만, 삽입/삭제가 느리다는 단점이 있다.
ArrayList를 사용한다면, 조회를 많이 하는 경우에 사용하는 것이 좋다
@Test
@DisplayName("Collection의 ArrayList 테스트")
void arrayListTest() {
List<String> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
arrayList.add("Hello");
arrayList.add("World");
assertEquals("World", arrayList.get(1)); // index를 이용하여 원소를 가지고 옴
assertEquals(2, arrayList.size()); // .size() 메소드로 크기를 가지고 옴
assertEquals("Hello World", String.join(" ", arrayList));
assertEquals("[Hello, World]", arrayList.toString());
}
LinkedList
LinkedList는 노드(Node)와 포인터(Pointer)를 이용하여 만든 리스트이다.
- 아래 Node 클래스를 보면 알겠지만,
next와prev로 양방향 포인터를 가진다

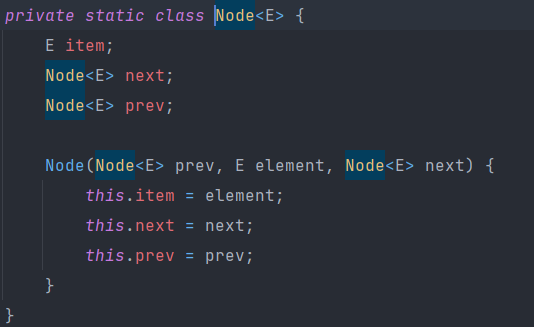
포인터로 각각의 노드들을 연결하고 있어서, 삽입/삭제가 빠르다는 장점이 있다.
- 단순히 기존 포인터를 끊고 새로운 노드에 연결하면 되기 때문에
하지만, 특정 원소를 조회하기 위해서는 첫 노드부터 순회해야하기 때문에 ArrayList에 비해 느리다는 단점이 있다.
LinkedList는 조회보다 삽입/삭제가 많은 경우에 사용하는것이 좋다.
@Test
@DisplayName("Collection의 LinkedList 테스트")
void linkedListTest() {
List<String> linkedList = new LinkedList<>();
linkedList.add("Hello");
linkedList.add("World");
assertEquals("Hello", linkedList.get(0)); // index를 이용하여 값을 가지고 옴
assertEquals(2, linkedList.size()); // size() 메소드로 리스트 크기를 가지고 옴
assertEquals("Hello World", String.join(" ", linkedList));
assertEquals("[Hello, World]", linkedList.toString());
}
Vector
Vector는 ArrayList와 같이 배열로 만들어진 리스트이다.

하지만, ArrayList와 다른점이 있는데, Thread-Safe하여 동기화를 지원한다
- 한번에 하나의 스레드만 접근이 가능
- Thread-Safe하여 멀티 스레드 환경에서 사용하기 좋다.
- 하지만, get, put에 모두 synchronized가 있어서, 스레드마다 lock이 걸리게되고 성능은 ArrayList에 비해 안좋다는 단점이 있다

참고로 Collections에서 동기화가 되는 콜렉션을 반환하는 synchonizedXXX() 메소드를 지원한다.
- 멀티스레드 환경에서 보통 Vector보단 아래와 같은 자료구조를 많이 쓴다.
Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>());
Collections.synchronizedSet(new HashSet<>());
Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap<>());
@Test
@DisplayName("Collection의 Vector 테스트")
void test() {
List<Integer> vector = new Vector<>();
vector.add(10);
vector.add(20);
vector.add(30);
assertEquals(10, vector.get(0));
assertEquals(20, vector.get(1));
assertEquals(3, vector.size());
assertTrue(vector.contains(10));
}
Stack
Stack은 LIFO(Last-In-First-Out) 특성을 가지는 자료구조이다
- 마지막에 들어온 원소가 처음으로 나가는 특징을 가진다.
- 들어올때는
push, 나갈때는pop이라는 용어를 사용한다.
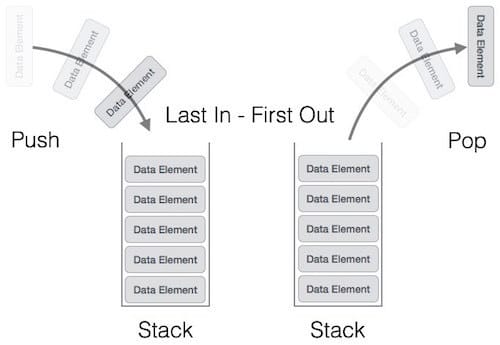
Stack은 Vector를 implements 받는다.
하지만 push()와 pop()은 Stack 클래스 내부에 구현되어 있기 때문에, 이 메소드를 사용하려면 Stack으로 받아야 함
@Test
@DisplayName("Collection의 Stack 테스트")
void stackTest() {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(30);
stack.push(50);
assertEquals(2, stack.size());
assertEquals(50, stack.pop());
assertEquals(30, stack.pop());
assertEquals(0, stack.size());
}
Collection - Set
Set은 집합이라고 부르며, 순서가 없고 원소의 중복을 허용하지 않는다는 특징이 있음
HashSet
HashSet은 집합의 특징 때문에 중복을 허용하지 않는다. 또한, 순서를 가지지 않음
- 대표적으로 많이 사용하는 집합(Set) 자료구조이다.
@Test
@DisplayName("Collection의 HashSet 테스트")
void hashSetTest() {
Set<Integer> hashSet = new HashSet<>();
hashSet.add(10);
hashSet.add(20);
hashSet.add(30);
hashSet.add(10); // 중복된 수 추가
assertEquals(3, hashSet.size());
assertEquals("[20, 10, 30]", hashSet.toString()); // 순서가 없음
}20
10
30
LinkedHashSet
집합의 특징은 중복을 허용하지 않고, 순서를 가지지 않는다는 특징이 있지만,
LinkedHashSet은 중복은 허용하지 않지만, 순서를 가진다는 특징이 있다.
@Test
@DisplayName("Collection의 LinkedHashSet 테스트")
void linkedHashSetTest() {
Set<Integer> linkedHashSet = new LinkedHashSet<>();
linkedHashSet.add(10);
linkedHashSet.add(20);
linkedHashSet.add(30);
linkedHashSet.add(10); // 중복된 수 추가
assertEquals(3, linkedHashSet.size());
// 들어온 순서대로, 순서를 가짐
Iterator<Integer> it = linkedHashSet.iterator();
while(it.hasNext())
System.out.println(it.next());
}10
20
30
TreeSet
TreeSet도 중복을 허용하지 않고, 순서를 가지지 않는다.
- 하지만, 데이터를 정렬하여 저장하고 있다는 특징이 있다.
@Test
@DisplayName("Collection의 TreeSet 테스트")
void treeSetTest() {
Set<Integer> treeSet = new TreeSet<>();
treeSet.add(20);
treeSet.add(1);
treeSet.add(100);
treeSet.add(33);
treeSet.add(1); // 중복 제거 됨
assertEquals(4, treeSet.size());
// 기본적으로는 오름차순으로 정렬 됨
Iterator<Integer> it = treeSet.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(it.next());
}
}1
20
33
100
Collection - Queue
Stack과는 다르게 FIFO(First-In-First-Out) 구조를 가진다.
- 처음 들어온 원소가 처음으로 나간다는 특징이 있음
- 들어올때는 enqueue, 나갈때는 dequeue라고 함

PriorityQueue
우선순위를 가지는 큐(queue)로 일반적인 큐와는 조금 다르게, 원소에 우선순위를 부여하여 높은 순으로 먼저 반환한다.
- 이진 트리 구조로 구현되어 있음
@Test
@DisplayName("Collection의 PriorityQueue 테스트")
void priorityQueueTest() {
// 오름차순 (default)
Queue<Integer> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>();
priorityQueue.add(2);
priorityQueue.add(30);
priorityQueue.add(100);
priorityQueue.add(1);
while(!priorityQueue.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println(priorityQueue.poll());
}
// 내림차순
Queue<Integer> priorityQueue2 = new PriorityQueue<>(Collections.reverseOrder());
priorityQueue2.add(2);
priorityQueue2.add(30);
priorityQueue2.add(100);
priorityQueue2.add(1);
while(!priorityQueue2.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println(priorityQueue2.poll());
}
}1
2
30
100
100
30
2
1
ArrayDeque
deque는 양쪽으로 넣고 빼는 것이 가능한 큐 자료구조이다.
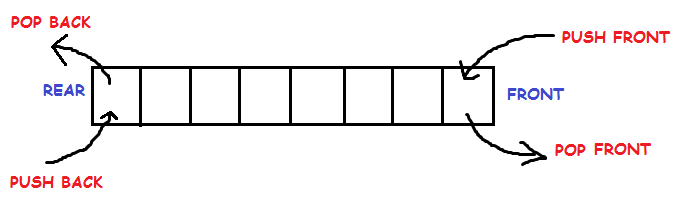
@Test
@DisplayName("Collection의 ArrayDeque 테스트")
void arrayDequeTest() {
Deque<Integer> deque = new ArrayDeque<>();
deque.offerLast(100); // 100
deque.offerFirst(10); // 10, 100
deque.offerFirst(20); // 20, 10, 100
deque.offerLast(30); // 20, 10, 100, 30
assertEquals(20, deque.pollFirst()); // 20 <- [10, 100, 30]
assertEquals(30, deque.pollLast()); // [10, 100] -> 30
assertEquals(10, deque.pollFirst()); // 10 <- [100]
assertEquals(100, deque.pollLast()); // [] -> 100
}
Map
Map은 Key와 Value로 이루어진 자료구조이다.
- Set과 같이 순서를 가지지 않음
- Key 값은 중복될 수 없지만, Value는 중복 될 수 있음

HashMap
HashMap은 일반적으로 많이 사용하는 Map 자료구조이다.
@Test
@DisplayName("Map의 HashMap 테스트")
void hashMapTest() {
Map<Integer, String> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put(1, "one");
hashMap.put(2, "two");
Iterator<Integer> it = hashMap.keySet().iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
int key = it.next();
System.out.println("key: " + key + ", value: " + hashMap.get(key));
}
}key: 1, value: one
key: 2, value: two
HashTable
HashMap과 동일한 특징을 가지지만, 차이점이라고 하면 Thread-Safe하여 동기화를 지원한다.
@Test
@DisplayName("Map의 Hashtable 테스트")
void hashtableTest() {
Map<Integer, String> hashtable = new Hashtable<>();
hashtable.put(1, "one");
hashtable.put(2, "two");
Iterator<Integer> it = hashtable.keySet().iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
int key = it.next();
System.out.println("key: " + key + ", value: " + hashtable.get(key));
}
}key: 2, value: two
key: 1, value: one
LinkedHashMap
일반적으로 Map 자료구조는 순서를 가지지 않지만, LinkedHashMap은 들어온 순서대로 순서를 가진다.
@Test
@DisplayName("Map의 LinkedHashMap 테스트")
void linkedHashMapTest() {
Map<Integer, String> map = new LinkedHashMap<>();
map.put(1, "one");
map.put(3, "tree");
map.put(2, "two");
map.put(4, "four");
map.put(5, "five");
Iterator<Integer> it = map.keySet().iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
int key = it.next();
System.out.println("key: " + key + ", value: " + map.get(key));
}
}key: 1, value: one
key: 3, value: tree
key: 2, value: two
key: 4, value: four
key: 5, value: five
TreeMap
이진트리로 구성되어 있고, TreeSet과 같이 정렬하여 데이터를 저장하고 있다.
데이터를 저장할때 정렬하기 때문에 저장 시간이 다른 자료구조에 비해 오래걸림
@Test
@DisplayName("Map의 TreeMap 테스트")
void treeMapTest() {
Map<Integer, String> map = new TreeMap<>();
map.put(1, "one");
map.put(3, "tree");
map.put(2, "two");
map.put(4, "four");
map.put(5, "five");
Iterator<Integer> it = map.keySet().iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
int key = it.next();
System.out.println("key: " + key + ", value: " + map.get(key));
}
}key: 1, value: one
key: 2, value: two
key: 3, value: tree
key: 4, value: four
key: 5, value: five'Language > JAVA' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Java - HashMap과 Hashtable의 차이 (0) | 2021.03.08 |
|---|---|
| Java - equals()와 hashCode()의 관계 (0) | 2021.03.07 |
| Java - String Pool에 대해서 (0) | 2021.03.07 |
| Java의 String과 StringBuilder, StringBuffer 비교 (0) | 2021.03.07 |
| JVM GC 동작 순서와 GC 종류(Serial / Parallel / CMS / G1 GC ) (0) | 2021.03.07 |
